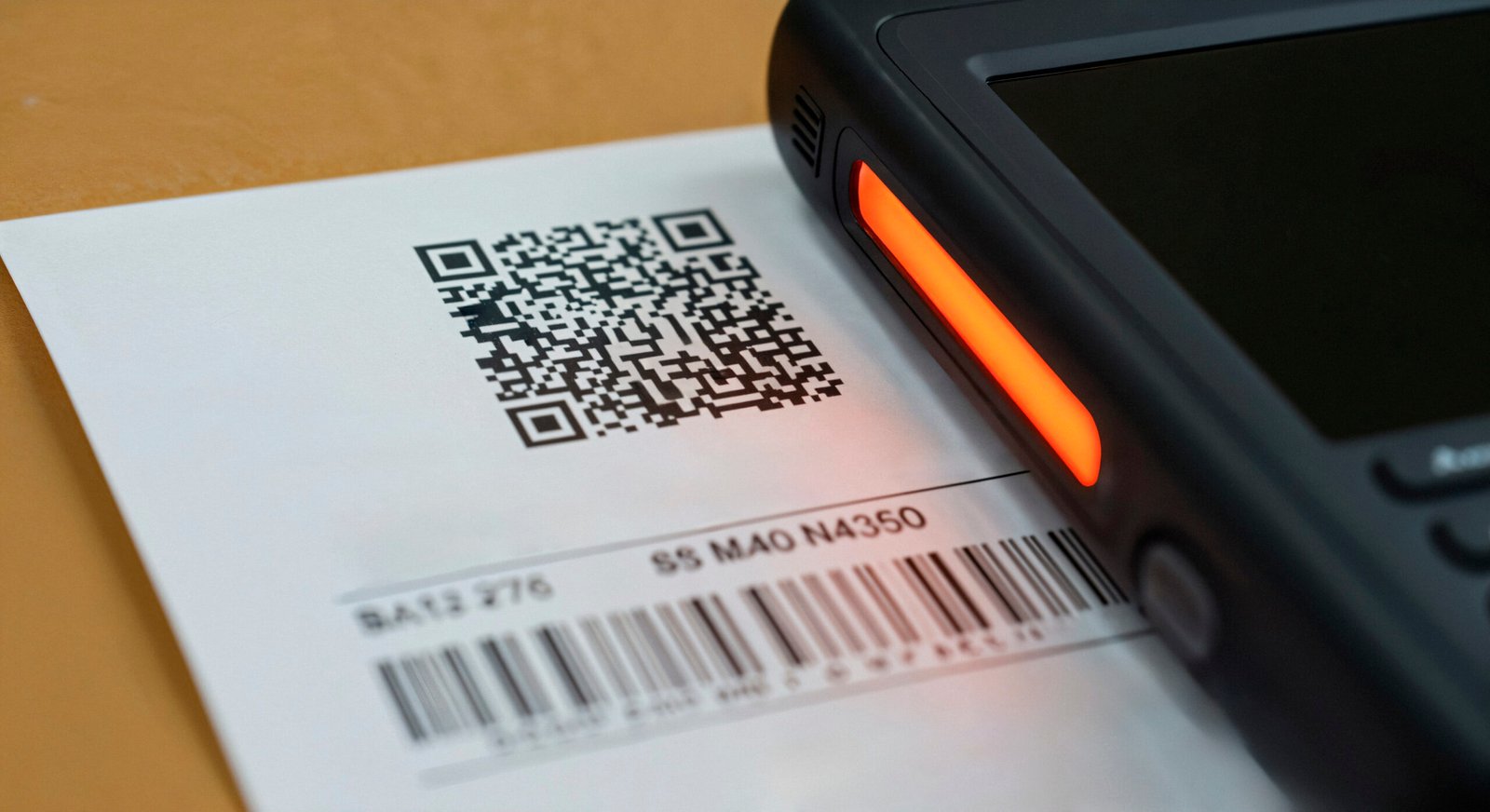
Every product you sell in the market encodes a barcode number, termed as GTIN or Global Trade Item Number. This number plays a crucial role in facilitating the unique identification of products in the market, both domestically and internationally.
But who provides this number and how? GS1 is the governing body of these numbers. It is the only global body that manages and implements standards concerning the supply chain, including those of identification and barcodes. It has 116 Member Organisations (MOs) affiliated with it, spread across 150+ countries. Each MO has a unique Country Code. GS1 India has ‘890’ as its Country Code.
Barcodes provided by GS1 India begin with ‘890’ in India. They are interoperable and are accepted across global supply chains. Let’s understand in detail what other components a barcode has in this blog.
What is a Barcode Number?
Now that we are aware of barcodes, let’s understand the life they carry – GTIN. Imagine if your PAN card does not have a PAN number associated with it. What will happen? The card will lose all its meaning. Similarly, take your Aadhaar card. What if it doesn’t have any Aadhaar number linked with it? Again, authorities will not be able to identify you in their logs. Sounds scary!
That is why the GTIN is essentially the lifeblood of a barcode. Without it, products cannot be identified, sold, purchased, or supplied in the market.
Structure of a GTIN
A GTIN has three components – the GCP (GS1 Company Prefix), Item Reference Number or Product Code, and the Check Digit. GCP can be further broken down into two parts – Country Code and Company Code. GTIN can have 12 digits, 13 digits, 14 digits, or 8 digits, depending on the product type and usage.
- GCP (GS1 Company Prefix):
This is a unique identifier assigned to a company by GS1 and can be further broken down into:
- Country Code: Indicates the GS1 Member Organisation that issued the prefix. While this may suggest the country where the company is registered, it does not necessarily reflect the country of origin of the product.
- Company Code: Uniquely identifies the brand owner or manufacturer.
- Country Code: Indicates the GS1 Member Organisation that issued the prefix. While this may suggest the country where the company is registered, it does not necessarily reflect the country of origin of the product.
- Item Reference Number (or Product Code):
This segment is assigned by the brand owner or manufacturer to identify a specific product or variation (e.g., size, flavour, colour). The number of digits allocated for this part depends on the length of the company prefix. - Check Digit:
This is the final digit of the GTIN, calculated using a standard algorithm (modulo 10) based on the preceding digits. It serves as a form of error detection to validate the accuracy of the GTIN during scanning or data entry.
A GTIN number may look like this –
8901234567895
Where ‘890’ is the country code, ‘123’ is the company code, ‘456789’ is the product code, and ‘5’ is the check digit.
GTIN is encoded in an EAN barcode. Read this blog to learn what an EAN/GTIN is.
GTIN Length Variants
GTINs come in different lengths depending on their application and packaging level:
- GTIN-8: Used for very small items with limited space for barcodes.
- GTIN-12: Common in North America (based on the UPC system).
- GTIN-13: Widely used globally, especially in retail environments (based on the EAN system).
- GTIN-14: Typically used for grouping trade items (e.g., outer cartons or cases).
Each variation adheres to the same basic structure but adjusts the lengths of the components.
Why is the Barcode Number Important?
- For Consumers: Identification of the barcode number is extremely important for consumers. When they validate a GTIN, they can ascertain if the product being sold to them is genuine or not. They can also fetch detailed information about the product with just one smartphone scan or by using future-forward tools like the Smart Consumer app.
- For Businesses: Barcodes are an effective tool in tracking, tracing, identifying, and also for managing inventories. Apart from this, it also enables efficient product identification and improved speed & productivity. For online platforms and marketplaces, a GTIN is often mandatory for product listings, enhancing searchability and credibility. Additionally, barcodes support traceability, helping businesses manage recalls and meet regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Barcode numbers play a vital role in ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and trust in today’s retail and supply chain systems. For businesses, they streamline operations and enable product traceability; for consumers, they help verify product authenticity and avoid counterfeits. With the right tools, finding and using barcode numbers is simple and accessible. Whether shopping online or in-store, paying attention to barcode numbers can help you make informed, secure purchases.









Leave a Reply